- Explore options like PyQt6, Tkinter, Kivy, and more for building powerful, interactive applications.
- OS compatibility, GUI needs, extension support, and community backing are essential for selecting a Python GUI framework.
- Transition from basic text-based applications to interactive, user-friendly graphical interfaces with Python
Top 8 Python GUI Frameworks for Developers
Published on: 12 February, 2026
Last updated on: 21 February, 2026
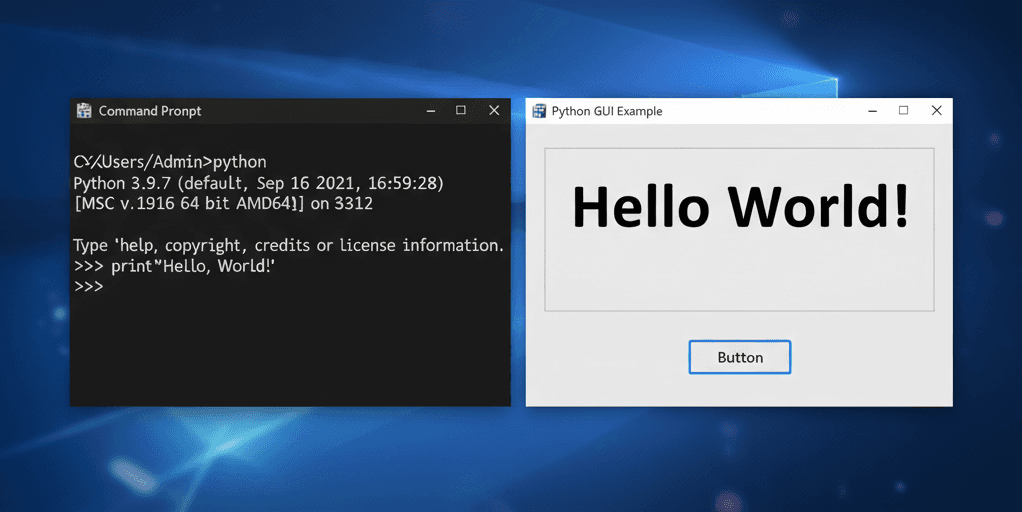
Have you ever built a Python app and realized it was a bit too basic? Maybe it only worked in the terminal with text-based commands, but you knew it needed something more, something interactive and user-friendly.
That's where GUI frameworks come in. They turn your simple app into something people can actually interact with buttons to click, windows to open, and data to explore. Choosing the right framework can make a huge difference, whether you’re creating a small desktop app or a mobile solution.
When I first started with Python, I built a simple inventory tracker. It was useful, but it only worked in the terminal, so I wanted to make it better. I tried Tkinter, the easiest GUI option, and was amazed when I saw my app pop up in a real window with buttons and input fields.
As my projects grew, though, Tkinter didn’t give me the flexibility I needed. I switched to PyQt6 and Kivy, which allowed me to create more complex, cross-platform apps. The transition made a huge difference, and I quickly saw how important it is to choose the right GUI framework.

Why Python GUI Frameworks Matter
Python is known for its simplicity, making it an excellent choice for beginners. But when it comes to building desktop or mobile applications that involve a graphical user interface, Python needs the help of external libraries, known as frameworks, to create intuitive and attractive GUIs. These frameworks provide pre-built tools for creating windows, buttons, labels, text fields, and other elements that form a user interface.
While Python offers some basic GUI capabilities, frameworks like PyQt, Tkinter, and Kivy extend its functionality and make it easy to create feature-rich, interactive applications.
Things to Consider When Choosing a Python GUI Framework
When deciding on the best framework for your project, there are key factors to consider:
- Platform Compatibility: Some frameworks work best on specific platforms, so ensure your choice aligns with the platforms you're targeting.
- GUI Needs: Understand what types of interactions and UI elements you need, such as buttons, forms, and input fields.
- Extension Support: Make sure the framework supports additional features like databases, multimedia, and APIs.
- Community Support: A strong, active community can help resolve issues quickly and provide resources for learning.
The 8 Best Python GUI Frameworks
1. PyQt6
PyQt6, built on the powerful Qt framework, allows rapid development of cross-platform applications with rich, modern user interfaces. It’s highly flexible, offering over 600 classes for GUI development.
Key Features:
- Cross-Platform: Works on Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, and Android.
- Integration: Easily integrates with SQL databases, XML processing, and multimedia applications.
- Qt Designer: A visual tool to design your UI faster.
Real-World Example:
Apps like Dropbox and Spotify were built using PyQt6, proving its performance and flexibility.
Pros:
- Excellent cross-platform compatibility.
- Large, active community.
- Supports modern features like multimedia integration.
Cons:
- Steep learning curve for beginners.
- Requires installation via PyPI, which can be challenging for newcomers.
2. Tkinter
Tkinter is Python's standard GUI library, offering a simple, straightforward way to build small applications. It’s great for beginners and small projects.
Key Features:
- Pre-installed: No need for extra installation—comes bundled with Python.
- Portability: Runs on Windows, macOS, and Linux.
- Lightweight: Great for simple, quick GUIs.
Real-World Example:
Tkinter is often used in educational projects and quick prototypes where speed is key.
Pros:
- Very easy to learn.
- No installation required.
- Cross-platform compatibility.
Cons:
- Limited customization for modern UIs.
- Outdated look compared to other frameworks.
3. Kivy
Kivy shines when it comes to developing touch-friendly, mobile applications. Its ability to handle gestures and support hardware-accelerated graphics makes it perfect for apps that require a lot of interactivity.
Key Features:
- Multi-Touch Support: Perfect for mobile apps.
- Cross-Platform: Supports Android, iOS, Linux, macOS, and Windows.
- OpenGL ES2 Acceleration: Provides smooth, high-performance graphics.
Real-World Example:
Startups and indie developers often use Kivy for mobile apps, including interactive art apps and games.
Pros:
- Ideal for mobile app development.
- Open-source with an active community.
- Very fast with hardware acceleration.
Cons:
- Non-native look and feel across platforms.
- Setup can be tricky for new users.
4. wxPython
wxPython offers native look-and-feel applications by using the underlying OS’s widgets. This makes apps built with wxPython blend seamlessly into each platform, from Windows to macOS and Linux.
Key Features:
- Native UI: GUIs look native on each platform.
- Cross-Platform: Works on Windows, macOS, and Linux.
- Extensive Widgets: From simple buttons to complex data grids.
Real-World Example:
wxPython is used by companies like Anaconda to create powerful data science tools that feel like native applications.
Pros:
- Native-like user interfaces.
- Cross-platform support.
- Extensive widget set for complex applications.
Cons:
- Can be slower for certain tasks.
- Installation can be cumbersome for beginners.
5. PySimpleGUI
For those who need a simple and easy-to-use GUI, PySimpleGUI abstracts away the complexities of other frameworks like Tkinter or PyQt and simplifies the code for beginners.
Key Features:
- Simplified Coding: Great for beginners and quick development.
- Cross-Platform: Works with Tkinter, Qt, wxPython, and Remi for web applications.
- Lightweight: Less code for building simple apps.
Real-World Example:
PySimpleGUI is commonly used for internal tools or quick prototypes where time is of the essence.
Pros:
- Very easy to learn and use.
- Open-source and cross-platform.
- Great for rapid prototyping.
Cons:
- Lacks flexibility for complex apps.
- Not ideal for large-scale applications.
6. PyGUI
PyGUI is a minimalist framework that provides just enough to create basic GUIs without much overhead. It’s perfect for simple applications that don’t need extensive features.
Key Features:
- Lightweight: Minimal code for basic applications.
- Open-source: Free to use and modify.
- Cross-Platform: Works on Windows, macOS, and Linux.
Real-World Example:
PyGUI is often used for small-scale desktop apps or interactive installations that don’t require complex interfaces.
Pros:
- Simple and efficient.
- Open-source.
- Cross-platform support.
Cons:
- No support for mobile apps.
- Limited features compared to larger frameworks.
7. Libavg
Libavg is built for multimedia and touch-based applications that require smooth graphics and high performance. It’s optimized for projects that need hardware acceleration.
Key Features:
- Touch-Based: Ideal for mobile apps.
- Hardware Acceleration: Ensures smooth performance.
- Multimedia Support: Perfect for image and video-heavy apps.
Real-World Example:
Libavg is used for interactive displays and digital signage solutions that need smooth graphics and touch functionality.
Pros:
- Best for multimedia apps.
- Hardware acceleration for performance.
- Supports multi-touch interfaces.
Cons:
- Limited documentation.
- Requires installation via pip.
8. PyForms
PyForms provides a minimalistic approach for rapid prototyping and building applications quickly with a simple API. It’s great for quick prototypes and small apps.
Key Features:
- Minimal API: Quickly build applications with minimal code.
- Cross-Platform: Works on Linux, macOS, and Windows.
- Fast Prototyping: Perfect for small, quick applications.
Real-World Example:
PyForms is perfect for internal business applications that need to be developed quickly.
Pros:
- Great for fast prototyping.
- Cross-platform support.
- Open-source.
Cons:
- Limited functionality for large applications.
- Doesn’t support mobile apps.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Python GUI Framework
Choosing the best Python GUI framework ultimately depends on your project’s needs, the complexity of your application, and your target platform. While Tkinter is great for beginners and small applications, PyQt6 and Kivy offer more advanced features for larger, cross-platform apps. If you’re focusing on mobile applications, Libavg is your best bet, while PySimpleGUI simplifies the process for rapid development of simple apps.
Remember, the right framework is crucial for your project's success, and making the right choice will ensure that you can build scalable, beautiful, and responsive applications. Whether you’re building your first app or developing something more complex, you now have the tools to make the right decision.
Need help with your Python project? Hire a dedicated Python team from Mediusware to bring your ideas to life with the right GUI framework. Get in touch with us today.
